Cardiac Tests in Houston, TX
There are a number of diagnostic tests that Dr. Alizera Nazeri and his staff perform to evaluate your heart function and detect heart rhythm disorders such as AFIB and other arrhythmias.
Echocardiogram
The two most common forms of an echocardiogram are:
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE)
This test is called a transthoracic echocardiogram because it is performed through the chest wall. The technician will place an ultrasound probe (transducer) on your chest and will move it over different areas of the chest wall to obtain images of your heart. The images are used to evaluate the heart muscle, the chambers of your heart, and the function of its valves in real time.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
This type of echocardiogram is performed by inserting a flexible tube with a transducer at its tip into your esophagus (the muscular tube that connects the mouth to your stomach). You will receive sedative medications to help you relax, after which the technician will insert the probe down your throat into your esophagus.
Because the esophagus is directly behind the heart, this test enables your doctor to get more detailed pictures of your heart and check for blood clots inside of it.
Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)

Cardiac Stress Test

During the test, you will be asked to exercise under the physician’s supervision, either on a treadmill or on a stationary bike, so that your heart function can be tested during activity.
Your doctor may combine the stress test with a complementary imaging test, such as a real-time echocardiogram (stress echocardiogram) or a test during which a special camera is used to create images of the blood flow to your heart (nuclear stress test).
Cardiac CT Scan
A cardiac computed tomography (CT) scan, or heart CT, is a noninvasive test during which X-ray technology is used to take detailed pictures of your heart, arteries, and other structures. During this test, you will be injected with an iodine-based solution called contrast material, after which the CT scan machine will be used to obtain images of your heart.
Your doctor may order this test to evaluate the structure of your heart, particularly the upper left chamber of the heart (left atrium) and the pulmonary veins before performing ablation for atrial fibrillation (Image 2).
The test can also detect coronary artery disease (narrowing or blockages of the arteries that supply the heart muscle with blood) and/or identify calcium buildup in the arteries, which can be an early sign of arterial disease (Image 1).
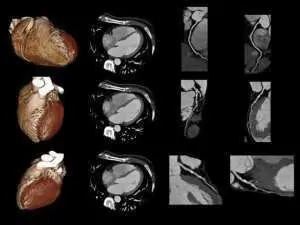

Cardiac MRI

Your doctor can use a cardiac MRI to look closely at the anatomy and function of different components of your heart, such as the upper left chamber (left atrium) and the pulmonary veins connected to it, the outer layers of the heart (pericardium), the heart valves, and the arteries that supply blood to the heart (coronary arteries).
This test is useful for planning procedures such as ablation of atrial fibrillation, as well as for diagnosing many heart conditions, including tissue damage (scar) caused by a heart attack and heart muscle diseases such as heart failure.
Coronary Angiography in Houston, TX

Cardiologists perform coronary angiography in a catheterization laboratory (cath lab). During the procedure, thin wires (catheters) are inserted into your heart arteries, usually through a femoral artery in your leg or through a radial artery in your arm. A solution called contrast material is injected to allow your doctor to evaluate your arteries with the use of X-rays (fluoroscopy).
If the coronary angiogram shows significant blockages, your doctor will recommend a coronary angioplasty or coronary artery bypass surgery to restore blood flow through the affected blood vessels.
Coronary angioplasty is performed to open clogged heart arteries. During this procedure, the cardiologist will insert a small balloon, guide it to the portion of your artery that is clogged and narrowed, and inflate it to help reopen the artery.
After unblocking clogged arteries, doctors often place permanent small mesh tubes called stents to keep the arteries open.
Tilt-Table Test
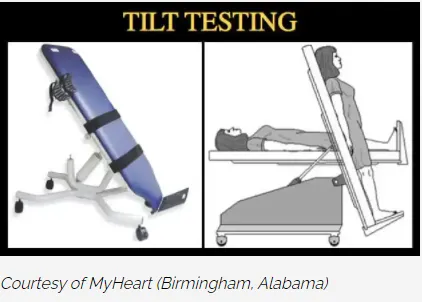
During the test, you will lie on an examination table that can raise your head 60 to 80 degrees above the rest of your body, while a nurse or doctor will continuously monitor the electrical activity of your heart (EKG), your blood pressure, and your heart rate.
If your blood pressure drops, you feel near fainting, or eventually pass out during the test, your result is considered positive. Your doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on the test results.
We offer comprehensive cardiac testing in our state-of-the-art office and affiliated hospitals in Houston, TX (at the Texas Medical Center). To learn more, please call us at (713) 909-3166 or Request an Appointment online.

